THE WORK OF CHARLES RICKETTS
PRE-RAPHAELITE!—the term is accepted, and
a singularly individual movement of
roman-
ticism in literature and art must needs be
content with the
ill-formed adjective. But
when one sets out on a career of apprecia-
tion of an artist who restricts himself to
this method of expression that
is not, and
never was, sympathetic to the masses, it is
with no hope
of convincing any one who
chances to be prejudiced against it. In writing
of art, the critic
writes merely to convince himself. When he sees his
vague
beliefs formulated in a sort of creed, it strengthens his own
and he feels, no doubt, that he is right; thus he is assured of
one convert
at least.
But although Mr. Charles Ricketts would probably not refuse
to call
himself a Pre-Raphaelite, if forced to adopt the
nickname of a great
school, yet it is also certain that his definition of
the aims and ideals
conveyed by that word would differ entirely from the
current accepta-
tion. The original Brotherhood have recorded their own
intentions
often enough—a whole literature of misrepresentation has also
gathered
round the school—so that it is best here to insist that the
Pre-
Raphaelitism of Mr. Ricketts is best understood by study of his
work.
In place of attempting to define the expression and show how
loyally
the artist obeys its most stringent rules, it were best to call
attention to
his method and his achievements, and let those who will deduce
the
creed from the practice. For any direct statement of
Pre-Raphaelite
aims and ideals seems doomed to be misinterpreted; one has
but to
turn to a journalistic notice of the Arts and Crafts movement, or
of
the Kelmscott Press editions, or to the criticism of any work
concerned
with decorative intention, to discover that all the qualities
which chance
to conflict with the writer’s own standard of taste are dubbed
impar-
tially ‘Pre-Raphaelite’ or ‘Impressionist,’ although for the most
part
unconcerned with either.
Nor is it needful here to trace the evolution of the
Pre-Raphaelite
illustration, under the hands of various
exponents, from The Germ
until it was almost
totally neglected. The best men of the new move-
ment, that supplanted it
for a while, contented themselves with a quiet
effort to attain
naturalistic effects without striving to keep their work
intensely
80
intensely strained in its expression
and full of spirituality. The Pre-
Raphaelite ideal has always insisted on
a high degree of nervous
tension, and this may be taken as the boundary
between two domains.
In 1870 the Graphic was started,
and with it grew rapidly a new
influence which, for a time at
least, caused the Pre-Raphaelite ideal to be
no more sought after. No
longer was there even a desire to represent
things, with every possible
circumstance, closely knit together in a
design meant to be pleasant to the
eye. In its stead, character in
isolation was the ruling motive, with just
enough actuality in the back-
ground to convey time and space. The pages of
Good Words or Once
a Week show this gradual change of front in men
working simul-
taneously. The drawings by Boyd Houghton form a connecting
link
between the old and new methods, the work of Sir John Millais
shows
also instances of both manners achieved with equal perfection; but
the
majority are attracted by newer gods. After the death of Boyd
Houghton, Pinwell, and Fred Walker, Charles Keene alone remained
faithful
to an entirely naturalistic convention, which at the same time
escaped the
mere prettiness that rapidly degraded the style of others.
The Dalziel Bible Gallery, a monumental attempt to bring
black
and white up to the level of its earlier triumphs, must
not be forgotten.
It is curious to find how this book, which to-day appears
to be what
modern jargon would style an epoch-making document, excited
no
great sympathy when it was published in 1881, and apparently failed
to influence the younger men who might have been expected to swear
allegiance to its principles. If you compare those illustrations with the
average work at the moment of its publication, you cannot fail to
realise
how wide a field has been traversed by English draughtsmen,
and how often
and how irresponsibly they have changed their aims.
For this work, prepared
many years previously, and detained by acci-
dental circumstances, retained
the stately phrase of a grander style.
Although its contributors showed
singularly unequal merit, the best bade
fair, even from their
accomplishment therein, to be ranked ultimately
among the great black and
white artists, irrespective of locality or date.
In his children’s toy-books, which have given their author a
wider
Continental reputation than most people imagine, Mr.
Walter Crane
created a new impulse. Voluntarily enlisting themselves under
the
standard he then set up, some twenty years after a school of
followers
have tardily sprung into being with alarming fecundity, a school
that is
satisfied for the most part if it can be decorative, ingenuous, and quaint.
Its
81
Its followers display, it is true,
a
certain inept alacrity, and no little
dexterity of a cumbrous sort, but
for
the most part lack entirely the real
fancy, or the naive humour
which
distinguishes the work of Mr. Walter
Crane’s best period.
Quite recently we have welcomed
the drawings by
Sir Edward Burne-
Jones, cut in wood for the Kelms-
cott Press
editions, and here and
there, both in England and on the
Continent,
are to be seen the first
attempts at a new renaissance of
the
Pre-Raphaelite idea, which,
born in England, and peculiar to
our
country, is nevertheless still
regarded as exotic, even by those
who
could so easily be better in-
formed.
The prominent place of Mr.
Ricketts in this
movement need not
be discussed here; it is already evi-
dent to many,
and because a large
number of these chance to be re-
moved from the
parochial influences
of contemporary criticism, it seems only logical
to accept their opinion
as the foreshadowing of a futur English
verdict. Lookers-on see
most of the game; yet it would be foolish to
set the verdict of the Con-
tinent in opposition to that of the current
periodical, were it not that
the one is the expression of artists, while
the other is chiefly that of
journalists.
That much of Mr. Ricketts earlier work is not accepted by
its
author as representative in any way, need not be urged
against him or
it. The unfettered illustrations, produced for no programme,
and
regardless of exterior criticism, may be said to begin with The Dial,
No. 1
82
No. 1, a magazine privately published,
in conjunction with some friends,
by the artist, then under the age of
twenty-one, at The Vale, Chelsea.
This sumptuous quarto, although
technically a private enterprise, was
sold to the public, and its limited
edition exhausted speedily. It found
appreciation not merely at home but
abroad, and despite its restricted
issue, has had no little influence on
contemporary workers. This was
soon followed by The
House of Pomegranates, a book which contains
illustrations,
together with the rather unsuccessful cover of peacocks in
gold and ivory,
entirely (with the exception of the full-page plates)
from Mr. Ricketts
hand. These display, no less surely than the Dial
illustrations, the peculiar individuality of his style. Later
on, the
Poems of Lord de Tabley, clad in a cover from his
design, contained
five elaborate illustrations which show the more
dramatic, the more
substantial, and the more really Pre-Raphaelite aspect
of his talent, and
are evidence of the survival of the Pre-Raphaelite idea,
still possessing
the vigour of its first imagination.
All these so far are pen-drawings, reproduced by process full
of
intricate dexterity, and abounding in elaborate conceits both
of idea
and technique. But another side of Mr. Ricketts art that has
engrossed
his attention for some years, and still appears to fascinate him
most, is
conceived in a very different mood. This work, invariably
engraved, by
its author, is imbued with the spirit of early Italian
wood-cutting, and
faithful to the convention developed by the artists who
illustrated the
Hypnerotomachia, the Quadriregio, and other Venetian and Florentine
books. In the
Vale editions of Daphnis and Chloe, a reprint of
Thorn-
leys translation of Longus’ idyll, and Marlowe’s Hero and Leander, the
illustrations throughout are not merely
designed, but cut in wood, by
the artist; and in their complete unity of
idea and handling must needs
prove extremely interesting, even to those who
fail to sympathise with
the spirit of their design. The marriage of art
with craft is peculiarly
popular among people who talk about the applied
arts to-day; but the
union often enough appears to be ill-assorted and
temporary. Here so
absolutely integral is the line conceived and the line
resulting, that you
cannot dissever them, even in thought. These
illustrations are severe
in their direct statement, suave in curve, and
full of lavish invention;
yet their effects are always gained by the most
reticent expression of
the idea. Courteous and scholarly, they do not aim
to astonish, or to
betray mastery of technique. It is surprising, indeed,
to compare the
Œdipus (a pen-drawing in the possession of Sir
Frederick Leighton)
here
83

here
repro-
duced, with
one of the
illustrations
to the poem
of The
Sphinx. In
the earlier
work, min-
ute
decora-
tion, ela-
borate
symbolism,
exquisite
daintiness of
finish, are carried to their final
utterance;
in the other,
the adventurous idea is curbed, and the
prodigal imagination brought
within the most restrained limits. The one
leaves unrecorded no facet
of the flashing crystal of the idea itself: the
most ingenious student
can scarce elucidate the many-sided presentation of
the subject
which is always consistently elaborated to develop the central
motive
of the composition, while its main intention is apparent at the
most
casual glance. In the other, the main purpose of the imagined
poem
in line is directly insisted upon, and reiterated without any
comments
or similes. Each class appeals to students; but whereas merely
intelli-
gent patience may unravel the first, to grasp the intention of the
second
demands a poetic vision hardly less keenly sustained than that of
its
author. Such work never has been, and is never likely to be,
popular
with the multitude. The simplicity of the commonplace they
under-
stand; the perplexity of the complex is also sufficiently dazzling
to
charm, if not to convince, them; but the final simplicity which is not
to
be appreciated without equal renunciation on the part of the
spectator
equal knowledge of his unexpressed but deliberate ignoring of
all
but the essential that can never appeal to any but those already
in touch with the idea. Merely to be misunderstood is no proof of
genius;
84
genius; bad grammar, or infelicitous
expression, may accomplish as
much; but to be misunderstanded of the
careless or ignorant, and
yet understanded of artistic people, has often
been the reward of an
artist.
Leaving for a moment the directly pictorial work, one has
only to
study his designs for covers, and the printed pages of
books produced
under his direction, to discover even stronger evidence of
his influence
upon younger men. True it is, that the new crusade to bring
together
the harmony of the type and its decoration cannot be credited
solely
to Mr. Ricketts in face of the achievements of the Kelmscott
Press.
But the artist, in the daring of youth, has combined intense loyalty
to
precedent, with experiment based on tradition. Saturated with know-
ledge of the past, his Pegasus has nevertheless shaken its wings and
essayed fresh flights. For his first manner, one has but to turn to a
prospectus issued to announce the advent of a new Dial, or to the
title-page of Silverpoints, or to still earlier books for which he is respon-
sible, to find absolutely new arrangements of older motives. Fantastic,
bizarre, and with splendid audacity, the unalterable tesserae of the
printers type are arranged in mosaics that depart from no single
tradition,
and yet reunite to display a score of fresh devices. In later
examples of
this class there is a marked change; despite the success of
his
improvisations, the importance of style is now more obviously felt,
obedience rather than invention is the aim. For this newer work,
despite
its original appearance, is built on ancient models to an extent
scarce
suspected by chance observers, because the artist has explored
the past
very thoroughly and discovered new models worthy of revival,
and deduced
from them new rules unsuspected heretofore. The
legerdemain of a Houdin,
prince of jugglers, dealt with gorgeous but
impossible objects cubes and
cones wrought with mystic devices, and
all the tinselled paraphernalia of
the property-man; that of the great
modern exponent of sleight-of-hand
astounds you the more, although
he juggles with the commonest objects of
the household. All your
wonder is called forth by the sheer artistry of the
consummate master,
and by no extraneous adjuncts. Mr. Ricketts effects, so
far, belong
to the latter class. From the ordinary types of the best
founders he
has evolved new triumphs, austere yet seductive, in detail
absolutely
obedient to self-imposed rules, but in massing and
architectural
arrangement, novel and vivid, as, for instance, in the Silverpoints before
mentioned.
Cloth-binding
85

Cloth-bind-
ing, but lat-
terly a thing
of horror, has
suddenly be-
come
illumi-
nated with
intelligence;
and for this
no second
name need be
coupled with
that of Mr.
Ricketts. In
his
splendid
decorations
for many mod-
ern books, too
familiar
to
people of taste
to need cata-
loguing here,
he has set
up
new stand-
ards that have
been largely
appreciated,
and unluckily
as largely imitated. Take, for instance, a
beautiful cover to one
of these books, with its three rigidly
symmetrical trees, and you will
see that a distinctly Eastern flavour
pervades it, yet the spirit of the
Renaissance infuses all to a sober
simplicity. The richness is obtained
by using certain contours and forms
sublimated to their most naive
expression. The straight lines of the tree
trunks, the absence of
any definition of the individual leaves, the
domestic fascination of the
tiny
86
tiny flowers, that might have been
raised in the garden oi a jeweller
all are contrived to afford a curiously
romantic pattern, that is old-world
in its essence but not in its handling.
For these covers contain an
entire rule of his own as to how metal stamps
should be understood in
the decoration of a book. If one looks at merely
technical facility in
employing the material wisely, the absence of any
pictorial detail, the
gorgeous effect of plain masses of gold upon the
subtly coloured cloths
chosen to receive the metal stamped upon its surface
all these sub-
ordinate items are worthy of appreciative study, for they
are not
accidental matters, left to the tradesmans fancy.
In the designs themselves one discovers sufficient material to supply
a
whole army of hungry designers, and leave many basketsful of
fragments to
be gathered up. Only a fellow-decorator can fully
appreciate this single
by-path of Mr. Ricketts art: only one who
has studied pattern-making can
entirely realise the new impetus he
has given to the craft. Hence it would
be foolish to indulge in
rhapsodies which would be superfluous to those who
know, and unin-
telligible to the rest.
That his work is prized abroad has been stated here before.
That
his wood-cutting is a sustained effort to preach anew a
truth out of
favour at present, is also patent enough; but in returning to
Mr.
Ricketts pictures in black and white, one must not forget to insist
on
the importance of recognising in them a gift of narrative that is
happily
allied to the research of handling. Invention and technique are
poised
in masterly balance. On purely typographical grounds one must
dis-
sect them, and note the well-arranged changes of line to suit the
type
destined to be set with the woodcut. Thus when the pictures (as
in
Lord de Tableys poems) are inserted as full-page plates, they fulfil
a
distinct pictorial convention, and hardly consider the type-page;
but
when (as in The Sphinx ) they are embedded
in the text, they are intensely
conventional, and entirely disdain the
naturalistic circumstances and
intricate workmanship of the earlier book.
Yet all the same they
equal the earlier fancies in complexity of idea and
intensity of situa-
tion. Planted among the type they forbear to arrogate
supreme
importance to themselves. Although dominating the page they do
so
with a courteous affectation of being merely decorative adjuncts;
yet
all the time they maintain their dignity unimpaired. In the
illustra-
tions to The Sphinx, where the type,
sparsely planned to decorate large
pages, supplies a modicum of text, the
pictures are also in delicate
lines,
91
lines, with masses of white to balance
and accord with the matter of
the book. The mere spacing of the pages and
the placing of the
pictures and text in this one volume would suffice, did
space permit, to
demonstrate the principle of balance and harmony which it
is the
peculiar aim of Mr. Ricketts to secure.
So much for their technical fascination. In their pictured
fancies
accompanying Poems Dramatic and
Lyrical, by Lord de Tabley,
you are not, as it were, confronted
by the plane of the white page.
Through it, you gaze into time and space
far removed from everyday
associations; and the glimpses of things scarce
known before brand
themselves deep into the memory, with all the
fascination of things seen
for the first time; for the artists power of
re-edifying the crumbled
palaces beyond the gates of ivory is akin to the
cunning of a slave of
the lamp. Take, for instance, the ‘Nimrod,’ and note
how the impas-
sivity of the stricken hero, with all the accidents of cloud
and flame, is
rendered more impressive by the oak-sprig in his girdle,
plucked from
the tree which has since fallen behind him. The lightning
still playing
on his crown, upon every metallic surface of his spear, and
the decora-
tion of his garments, leaves no doubt of the source of the
catastrophe.
Nor must one fail to recognise the tact of the artist in
closing the eyes
of the man, who seems to be the only thing remaining alive
when all
has crumbled about him. To analyse these more minutely, it is
interesting to compare the different treatment of the nerveless hand of
the
Nimrod who has dropped his shield with the searching hands
of the figure
that represents Death (in the frontispiece ‘Death of
the Old King’). Nor
should one fail to notice the fantasy that
depicts this figure picking a
laurel wreath to pieces, leaf by leaf, nor
the admirable conceit in
crowding his lap full of love-letters and locks
of hair.
The designs for a forthcoming edition of Apuleius’ Golden Ass,
some of which are here
given before being cut on the wood, fulfil
very different conditions. There
is an ingenious touch in making
Psyche pensive before the painted
representatives of the Loves
of the Gods, and one that does not lack
humour, elsewhere a not
unusual quality in the artists work, although
rarely evident on the
surface.
But it would be almost impertinent to attempt to compile a
guide-
book to the wonderland of Mr. Ricketts imagination. Only
a poet can
fully gauge the whole of a poets meaning. One must remember that
months
92
months of patient thought in
elaborating the germ of an idea, and then
presenting it in a way purposely
sublimated and reduced to its most
meagre essentials, leave no result that
he who runs may read. Great
ideas slowly shaped require no little study to
realise their concealed
variety.
As a last word, it may be wise to say that, in the
illustrations here
reproduced, we see but one side of Mr.
Ricketts art. For, with a single
exception, they are all reproductions of
pen-drawings made for process,
or drawings intended to be, but not already,
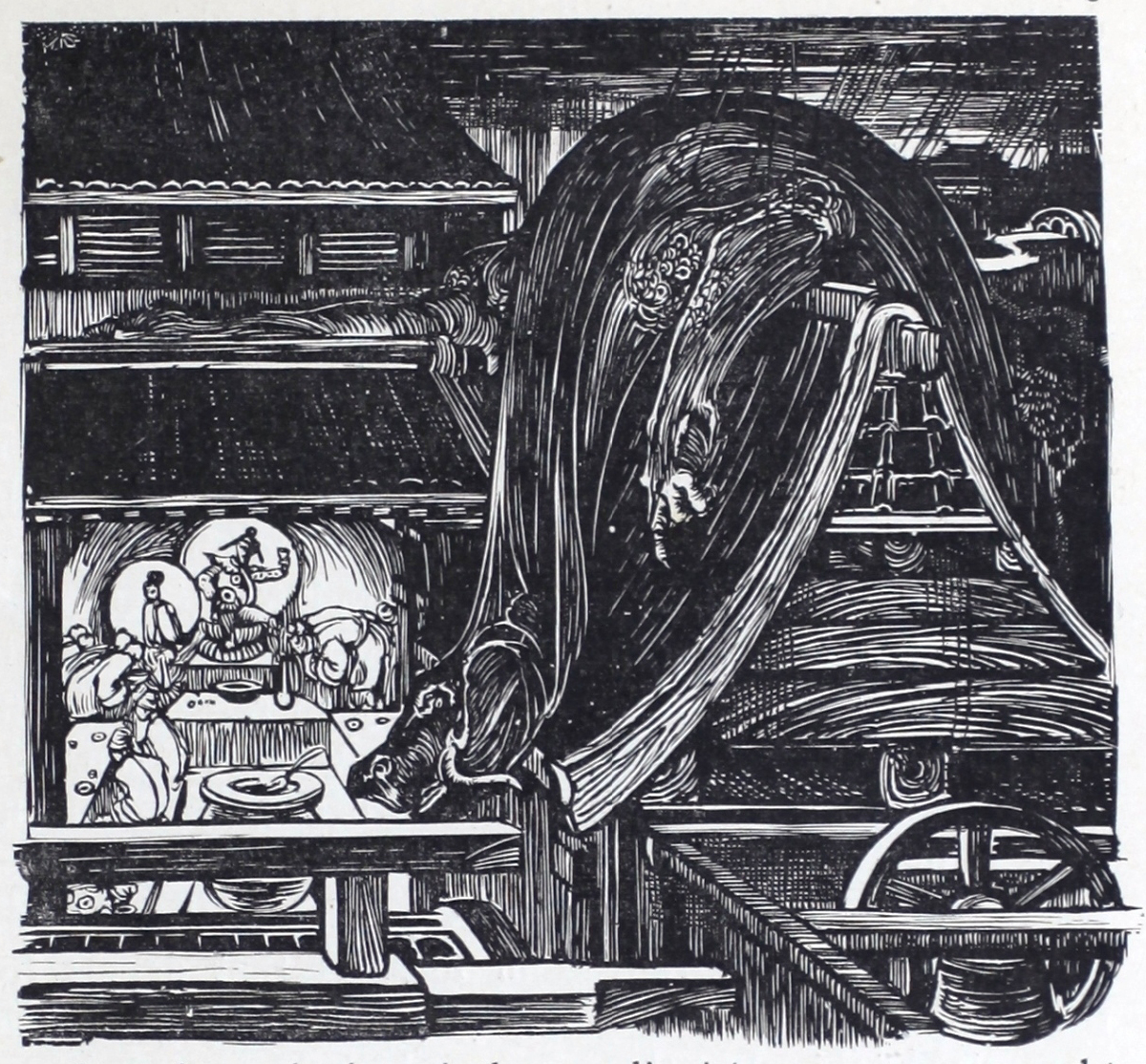
cut on wood. The little
dragon on the roof affords a solitary example of
his most expressive
manipulation of the yet unappreciated line of the
wood-block. The
etchers line has been the subject of many rhapsodies; but
the line of
the great wood-engraver is still to be commemorated by a
perfect
eulogy. A line that varies from that of Diirer to the white line
of
Linton, that can imitate the nervous accent of the brush of
Hokosai,
or accord gracefully with the labial fluid curves of the great
Italians, a
line that ranges from the wooden inelegance of the journeyman
en-
graver to the sentient, emotional touch of Mr. Ricketts, is of no
slight
importance. It can be the meanest or the most beautiful of
lines,
according to the handling of the one who cuts it, and let us not
forget
that, unlike the Japanese engraver and the dexterous American
en-
gravers, Mr. Ricketts invents the work to be cut; that, even in
the
past, such men are few in number, and that he already has his
following.
It is of less importance to decide whether the art of
wood-cutting
is dying out for popular use, or is being restricted to the
highest
employment only from the commercial rivalry of process work.
While an artist so accomplished and withal so reticent in the
mere
virtuosity of his craft handles it as Mr. Ricketts can, one
need not fear
for its immediate future, or doubt that the end of the
nineteenth century
will leave new masterpieces for the cabinets of
future collectors.
The apparently unproductive years, since the last Vale
books
appeared, do not imply cessation of creative work, but
rather denote
the conception and elaboration of a new enterprise. Amid the
group
of books not merely illustrated, but planned in every detail by
Mr.
Ricketts which are on the eve of publication, with a type of his
own
designing, will be found some notable works that will more than
justify
the appreciation here set down clumsily, if truly.
The courage of ones convictions has been unduly praised; the
really
praiseworthy
93
praiseworthy attitude is surely to
possess the undoubted conviction
of one’s courage. Yet as the first person
who tells the truth before its
time is usually held to be a proved liar
thereby perhaps it would
have been more seemly to refrain from an attempt
to formulate opinions
not yet accepted by all men of light and leading,
although one has no
doubt of the final verdict. For an artist so individual
and distinctly
true to his own ideals, no matter what they may be, as Mr.
Ricketts
assuredly is, will certainly receive complete appreciation
ultimately from
those who can consider his work dispassionately, with full
documentary
evidence of the influence it exerted on his successors, and its
relative
position among contemporaneous efforts.
GLEESON WHITE.
MLA citation:
White, J. W. Gleeson. “The Work of Charles Ricketts.” The Pageant, 1896, pp. 79-93. Pageant Digital Edition, edited by Frederick King and Lorraine Janzen Kooistra, 2019-2021. Yellow Nineties 2.0, Ryerson University Centre for Digital Humanities, 2021. https://1890s.ca/pag1-white-ricketts/
![The ornamental border is positioned to the left of the text and is oriented vertically, extending the full length of the letterpress. The capital letters “SPES” [alluding to the Roman goddess Hope] are engraved in a wooden cartouche above the ornament, so that the scene appears to be depicted within the architectural space of a wooden room or portico. Centred within this space is a naked woman with long hair standing on the top of two wooden steps. The woman is leaning on the wall to her right and is looking downwards to the left at the flaming torch she is holding with both hands. Rays of light emerge from the flame and radiate downward in diagonals across the majority of the ornament’s bottom left half. Behind the woman’s left shoulder is a small window in which a single star appears. To the woman’s right, there is white paneled door with a mullioned window. A banner is draped in front of the window. In the extreme foreground to the right of the steps is a wooden balustrade with a domed head covered in vines. A white dove is depicted flying through the middle, lower half of the ornament. Small crocuses and other flowers line the base of the ornament. In the bottom left corner, the artist's initials “CR” are engraved on a small white square. Beneath them the year “1889” appears.](https://1890s.ca/wp-content/uploads/white-ricketts-intxt-p81.jpg)